At A Glance
| End Result: | After a month |
|---|---|
| Socially fit: | After 2 to 3 days |
| Fit for desk work: | After 2-3 days |
| Surgery: | Local anaesthesia or general anaesthesia |
| Risk: | Low |
| Pain: | Low |
| Active exercise: | After 2 weeks |
| Inconveniences: | Some bruising, swelling and soreness which lasts for a few days |
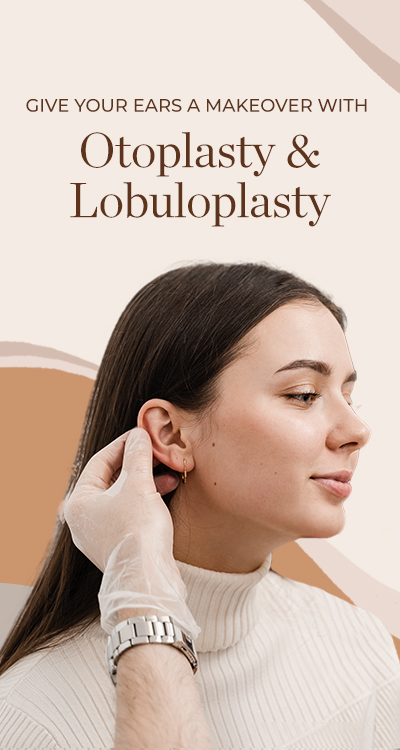
What is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty, commonly known as ear surgery or ear pinning, is a cosmetic procedure aimed at reshaping and repositioning the ears to improve their appearance. Otoplasty can address a variety of concerns related to the size, shape, or position of the ears, including protruding ears, oversized ears, asymmetrical ears, or ears with congenital deformities. During otoplasty, the surgeon may reshape the cartilage of the ears and manipulate the position of the ears closer to the head to create a more balanced and proportionate appearance. This procedure is typically performed under local or general anaesthesia on an outpatient basis and can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and confidence by improving facial harmony and symmetry.
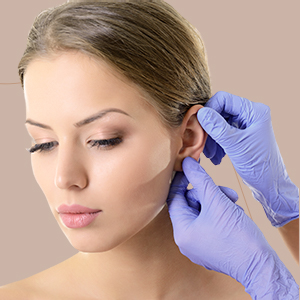
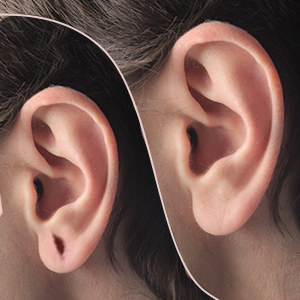
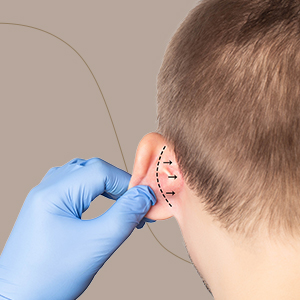
Why Otoplasty?
Otoplasty is suitable for individuals who are bothered by the appearance of their ears and wish to enhance their facial aesthetics by addressing issues such as protruding or asymmetrical ears. Ideal candidates for otoplasty are typically in good overall health, have realistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure, and are seeking to improve their self-image and confidence. Children and adults who experience teasing or bullying due to the appearance of their ears may benefit from otoplasty to correct prominent or misshapen ears and achieve a more natural and proportionate ear contour. Additionally, individuals with congenital ear deformities or injuries that affect the appearance of their ears may consider otoplasty to restore symmetry and enhance facial harmony.