
At A Glance
| End Result: | After a few months |
|---|---|
| Socially fit: | After 2-3 days |
| Fit for desk work: | After 5-7 days |
| Surgery: | General Anaesthesia |
| Risk: | Low |
| Pain: | Low |
| Active exercise: | After 3-6 weeks |
| Inconveniences: | Initial bruising, swelling, compression garment to be used for 4 weeks |
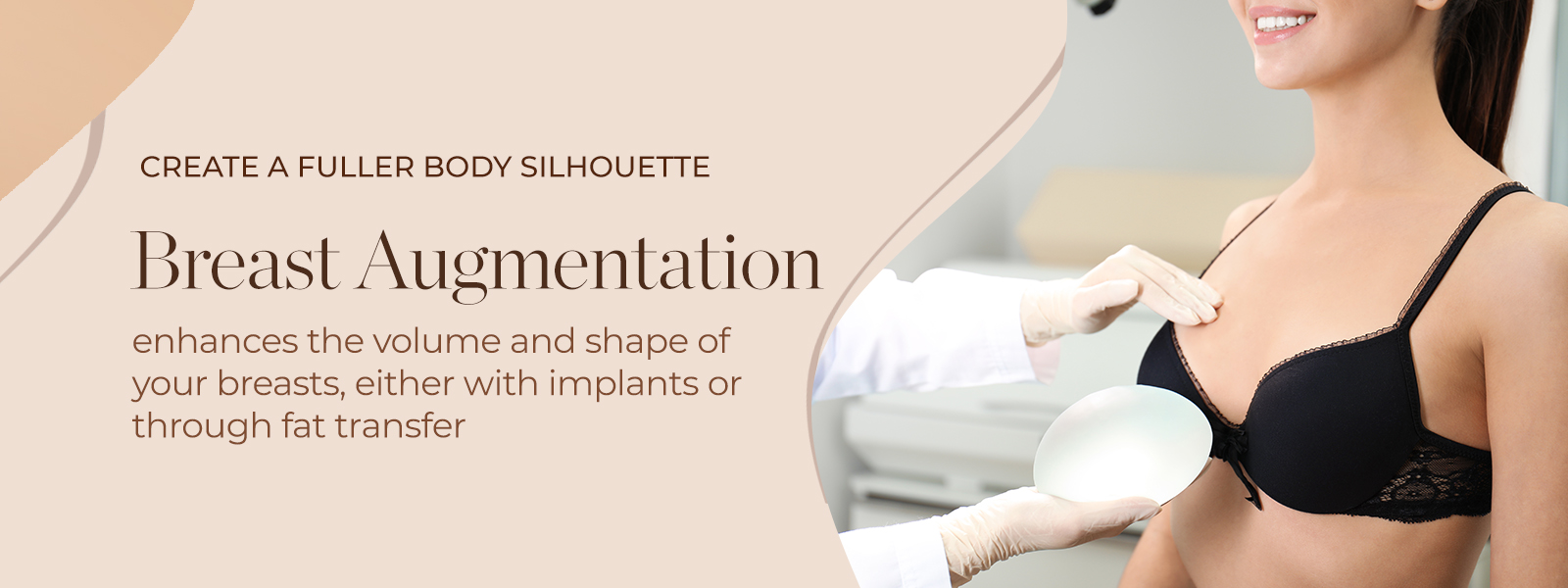
What is Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at increasing the size, enhancing the shape, or improving the symmetry of the breasts. This cosmetic surgery involves the placement of breast implants or the use of fat transfer techniques to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome. Breast implants are typically filled with saline or silicone gel and come in various shapes, sizes, and textures to accommodate individual preferences. The procedure may also involve incisions made either around the areola, in the inframammary fold, or in the armpit, through which the implants are inserted and positioned either under the chest muscle (submuscular) or directly behind the breast tissue (sub-glandular). Breast augmentation is a highly customizable procedure that aims to enhance breast volume and projection, improve body proportions, and boost self-confidence.


Why Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation is suitable for individuals who are dissatisfied with the size, shape, or symmetry of their breasts and desire enhancement for aesthetic reasons. Ideal candidates for breast augmentation are typically in good overall health, have realistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure, and are seeking to improve their self-image and confidence. Women may consider breast augmentation if they have naturally small breasts, asymmetrical breasts, or breasts that have lost volume and firmness due to factors such as pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight loss, or ageing. Additionally, breast augmentation may be an option for individuals who have undergone mastectomy or breast reconstruction and wish to restore breast volume and symmetry.